A satellite is any object that orbits another, larger object in space.

Does any of the above represent satellites?
A satellite is any object that orbits another, larger object in space.
What is an Orbit?
An orbit is the curved path that an object in space takes around another object due to gravity.
This happens in a way that is similar to throwing a ball out of the window of a tall tower – to get the ball going, you need to first give it a ‘push’ by throwing it, making the ball fall towards the ground on a curved path. Whilst it is your throw that gives the ball its initial speed, it is gravity alone that keeps the ball moving towards the ground once you let go.

But what if we say, no object in space orbits around an object?
It's about something called the Barycenter. Learn more from the folks at NASA: Barycenter
With the definition in mind, can you think of every object that goes around a larger object in Space?
Lets get to the next section for examples of what can be termed satellites.
These are naturally formed celestial bodies that orbit another, larger celestial body. For example, the Moons of a planet, planets of a star, etc.
Some examples of natural satellites from our Solar System.

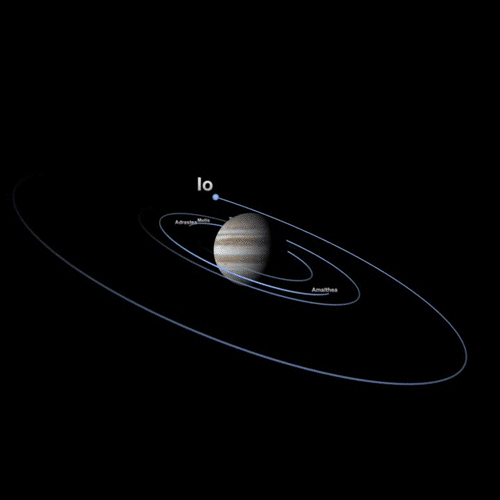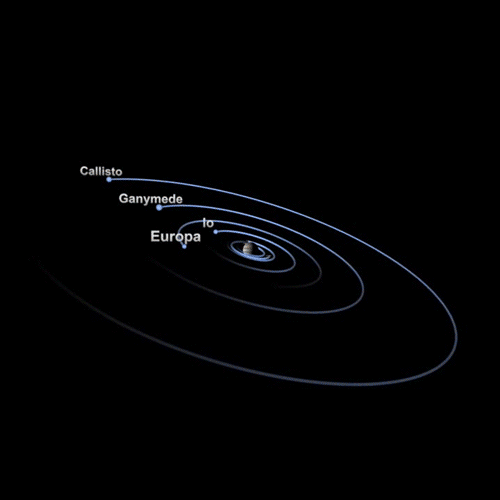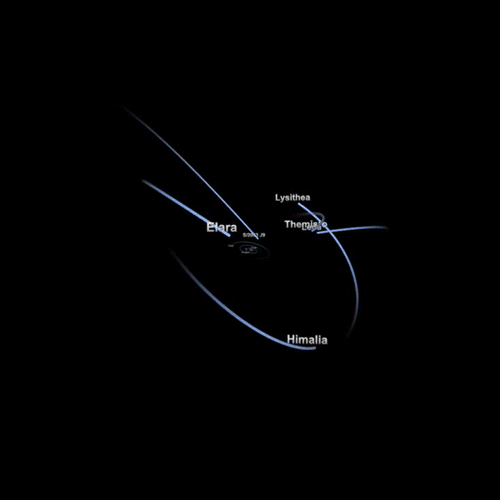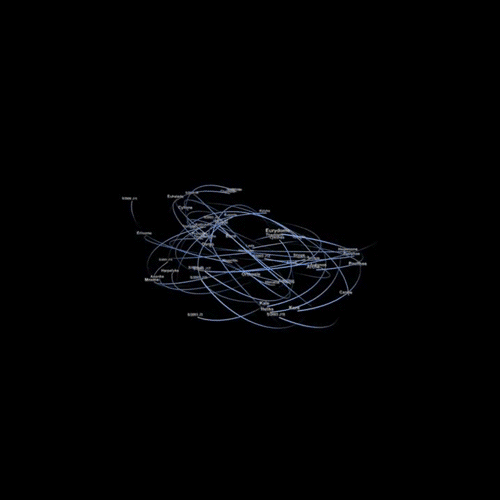
Is Earth a satellite too?
These are man-made devices that are launched into space and orbit the Earth or another celestial body. They come in many shapes and sizes and are designed for various purposes.

Observe the differences in each of the satellites above.. Does all satellites look some & do the same work?
"Artificial Satellites are man-made devices that are launched into space and orbit the Earth or another celestial body. They come in many shapes and sizes and are designed for various purposes."
Pioneers of artificial satellite
The idea and realization of the artificial satellite were collaborative achievements of visionary thinkers and dedicated scientists. Konstantin Tsiolkovsky, often termed the "father of astronautics," introduced the concept of space stations orbiting Earth in the early 20th century. Though Tsiolkovsky laid down theoretical foundations, it was Sergei Korolev, known as the chief architect of the Soviet space program, who brought this vision to life.
Under Korolev's leadership, the USSR successfully launched the world's first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, on October 4, 1957. This monumental achievement wasn't the result of one individual's effort but a collective endeavor by a team of scientists, engineers, and technicians.
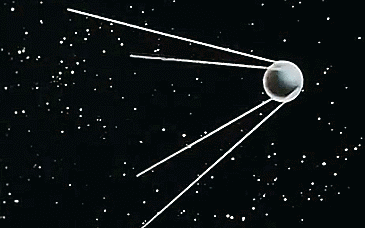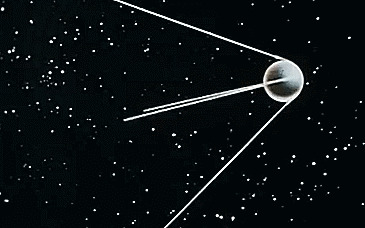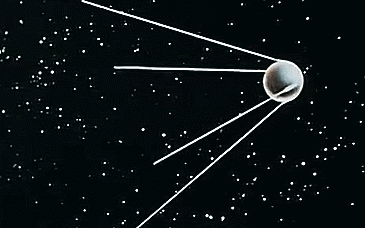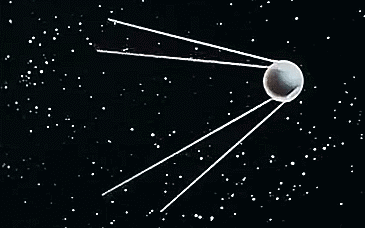
What are parts of an artificial satellite?
It's about something called the Barycenter. Learn more from the folks at NASA: Barycenter
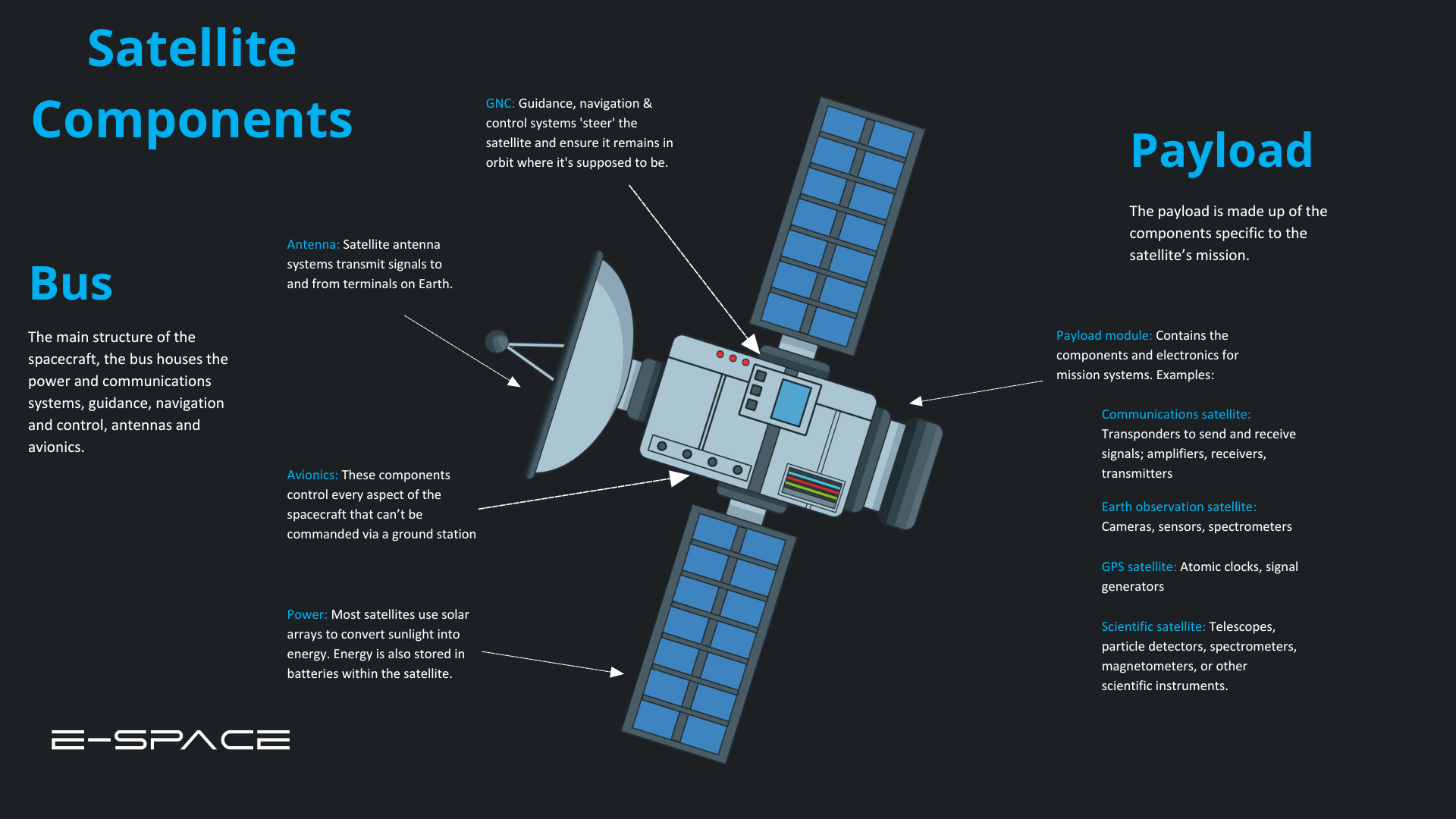
Can you think of what applications can we derive from an object orbiting a bigger object? We will explore them next..
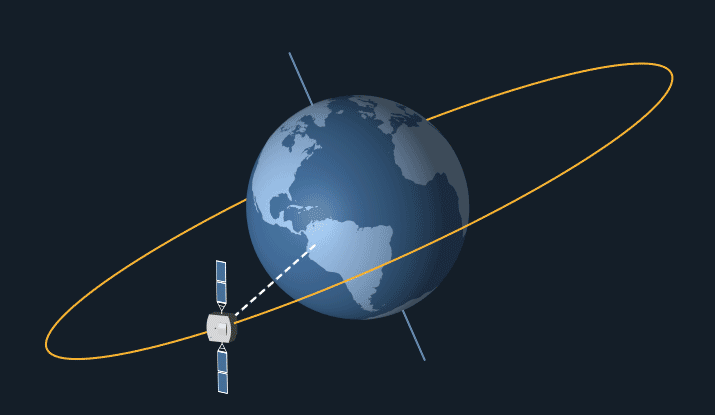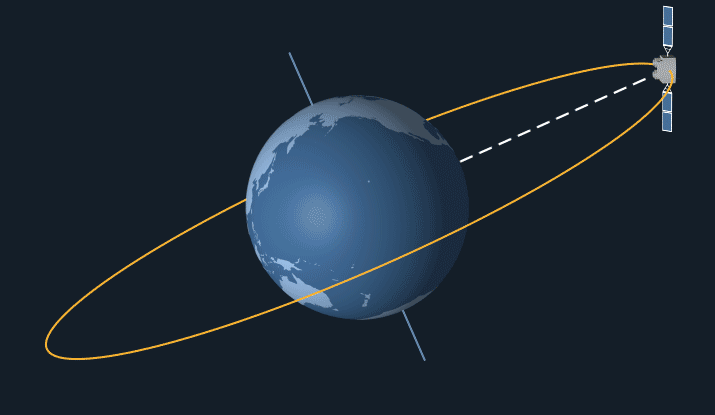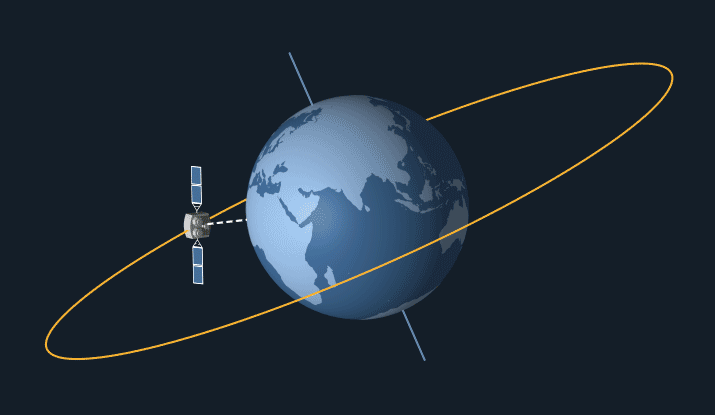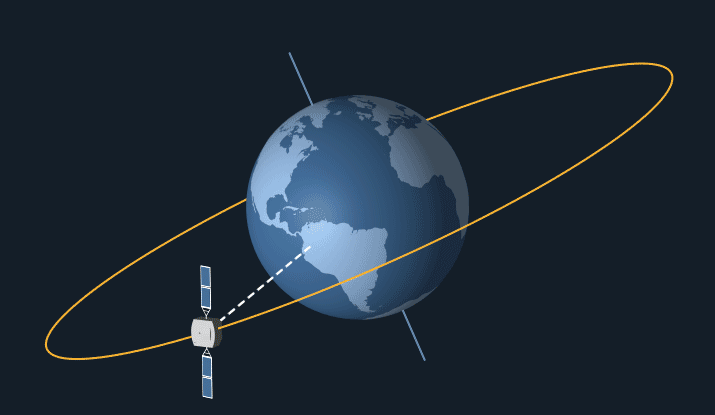
Orbits are paths taken by satellites around a celestial body, such as Earth. The type of orbit is characterised by its shape, inclination & distance from the surface of celestial body.
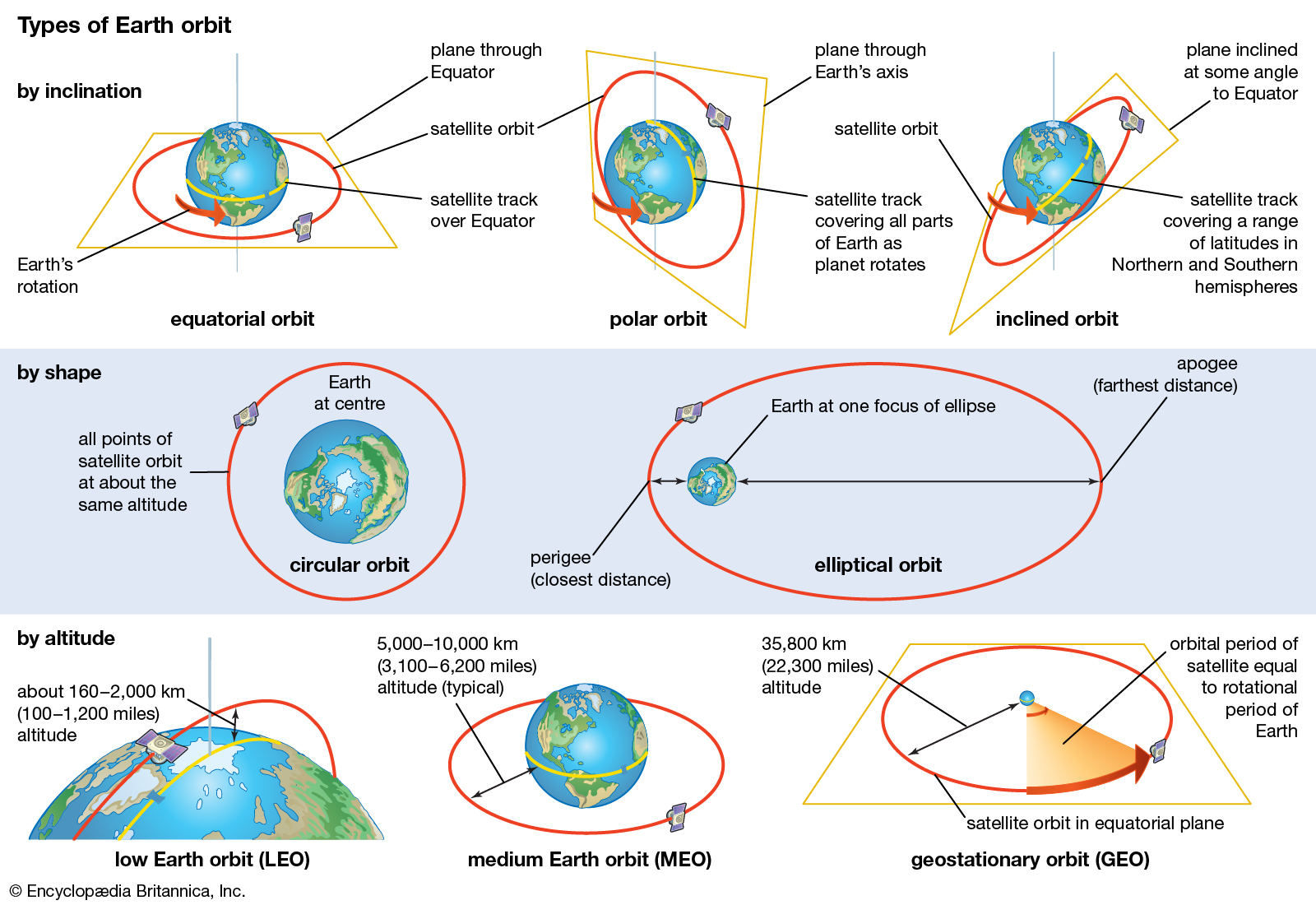
GEO (Geostationary Orbit)
LEO (Low Earth Orbit)
MEO (Medium Earth Orbit)
GTO (Geostationary Transfer Orbit)
Polar Orbit
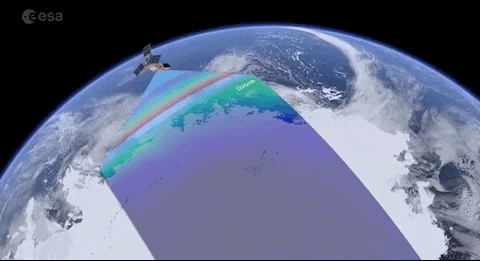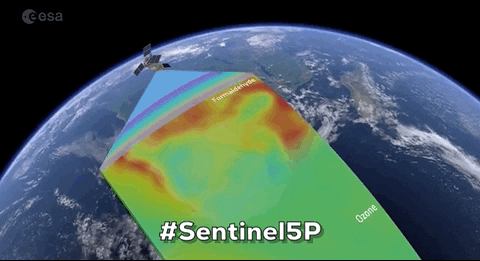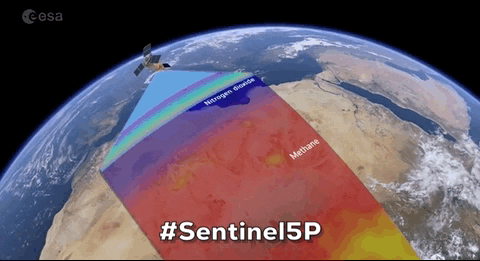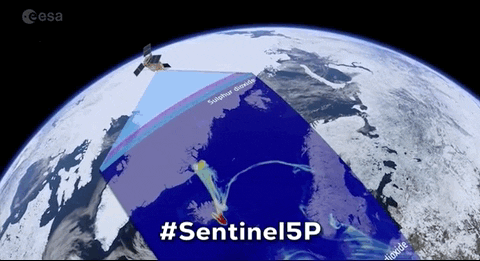
Satellites specifically designed to observe Earth from orbit, typically for environmental, meteorological, and strategic purposes.

"Satellites specifically designed to observe Earth from orbit, typically for environmental, meteorological, and strategic purposes."
Orbits
Instruments

Applications
Satellites designed to facilitate various forms of communication, including voice, data, and television broadcasting, by relaying signals between transmitters and receivers on Earth.

"Satellites designed to facilitate various forms of communication, including voice, data, and television broadcasting, by relaying signals between transmitters and receivers on Earth."
Orbits
Key Features

Applications
Indian Communication Satellite Examples
Satellites specifically designed to provide Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) services, enabling precise positioning, navigation, and timing information to users on the ground, in the air, and at sea.

"Satellites designed for Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) services, enabling precise positioning, navigation, and timing."
Orbits
Key Components

Applications
These are satellites or probes designed for scientific research, either about the Earth's environment, outer space, or other celestial bodies. Their primary purpose isn't commercial but mainly to expand human knowledge.

"Satellites designed for scientific research about Earth's environment, outer space, or celestial bodies."
Orbits & Destinations
Instrumentation
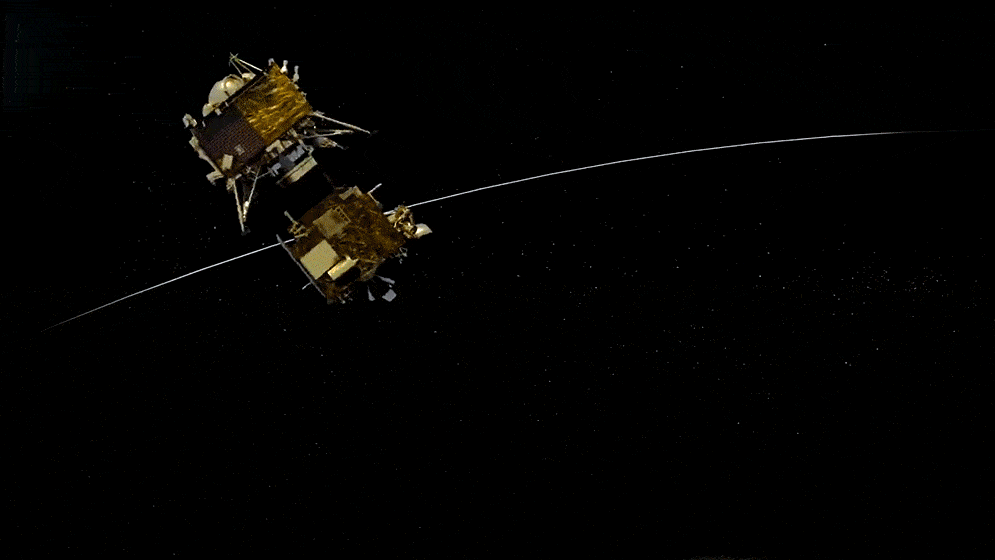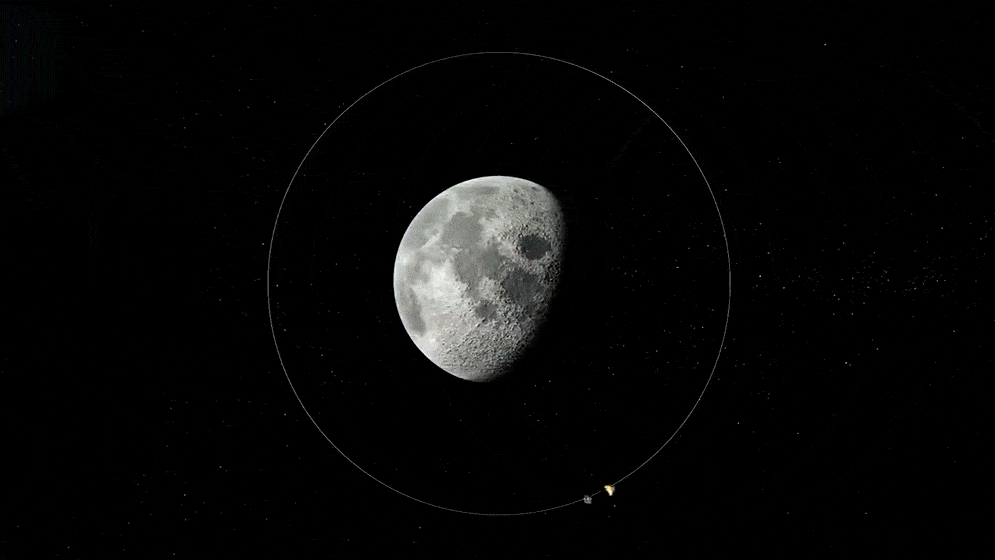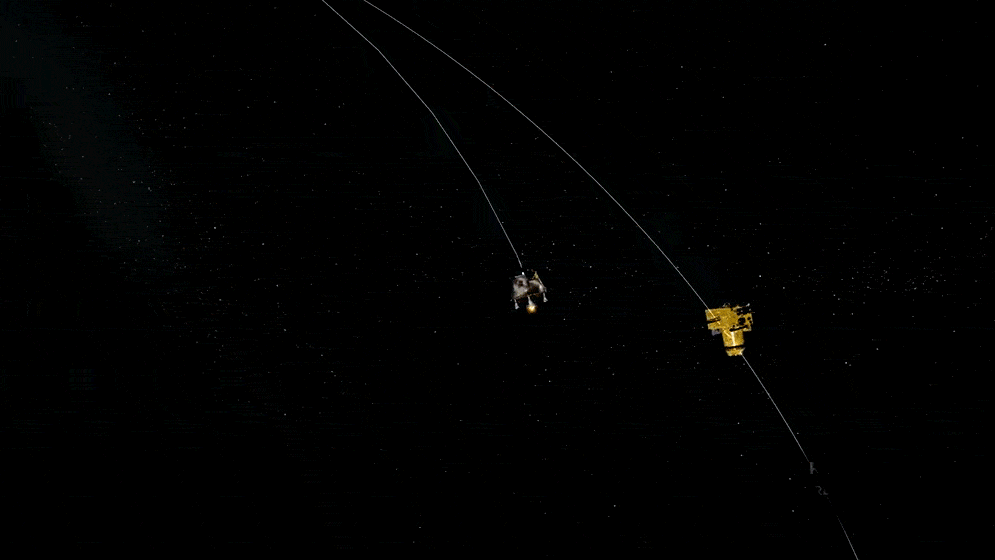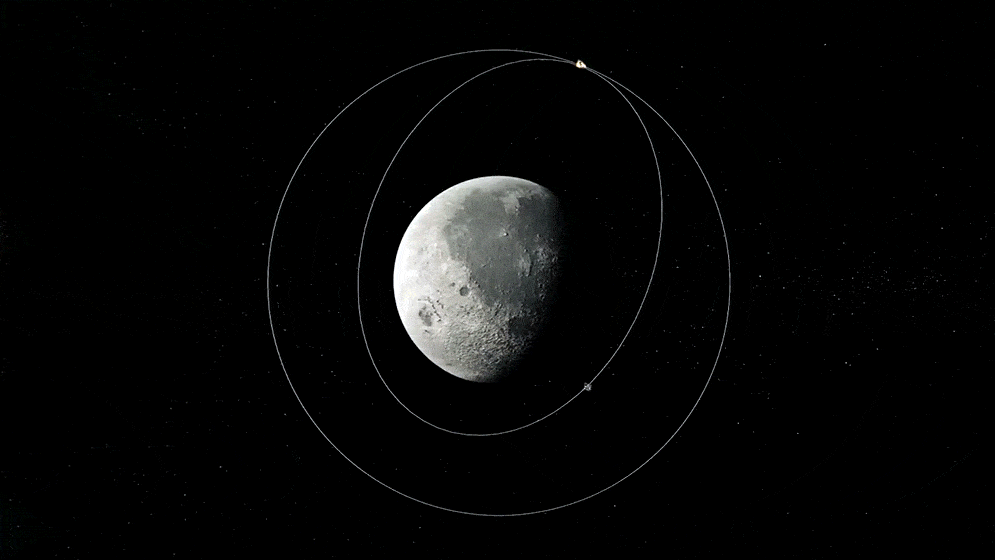
Applications
Indian Satellite Examples
SatelliteXplorer - a tool to summarize everything we learnt so far visually : Click here
Cubesat 101 : Full process Click here